Advanced Search
Content Type: Long Read
In this piece we examine mobile phone extraction, relying on publicly available information and Privacy International’s experience from conducting mobile phone extraction using a Cellebrite UFED Touch 2. We welcome input from experts in the field. This is a rapidly developing area. Just as new security features are announced for phones, so too new methods to extract data are found.
[All references can be found in the pdf version below.]
General explanation of mobile phone…
Content Type: Long Read
Photo by Nadine Shaabana on Unsplash
Digital identity providers
Around the world, we are seeing the growth of digital IDs, and companies looking to offer ways for people to prove their identity online and off. The UK is no exception; indeed, the trade body for the UK tech industry is calling for the development of a “digital identity ecosystem”, with private companies providing a key role. Having a role for private companies in this sector is not necessarily a problem: after all, …
Content Type: News & Analysis
Photo by Daniel Jensen on Unsplash
Everyone is talking about Facebook's end-to-end encryption plans and the US, UK and Australian government's response. Feeling lost? Here is what you need to know.
What's Facebook trying to do?
First let's be clear: Facebook has many faults when it comes to privacy. It's also suffered a number of security failures recently. See here for instance.
In response to their successive failures to protect your privacy, Facebook announced in their 'pivot to privacy…
Content Type: Long Read
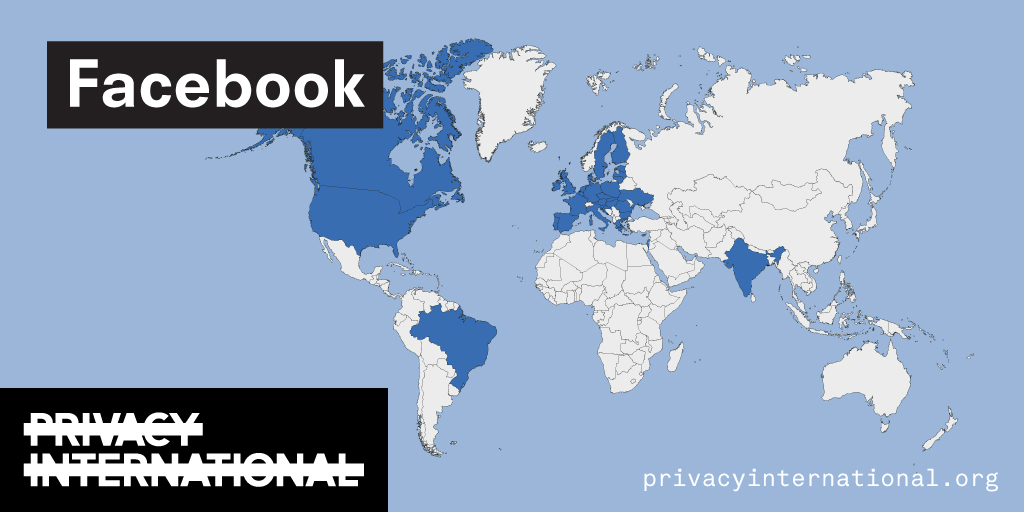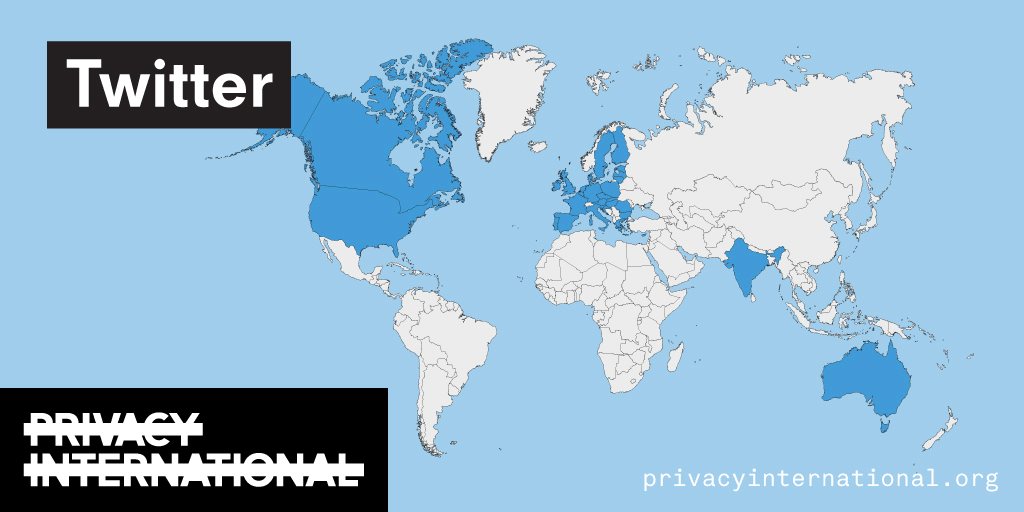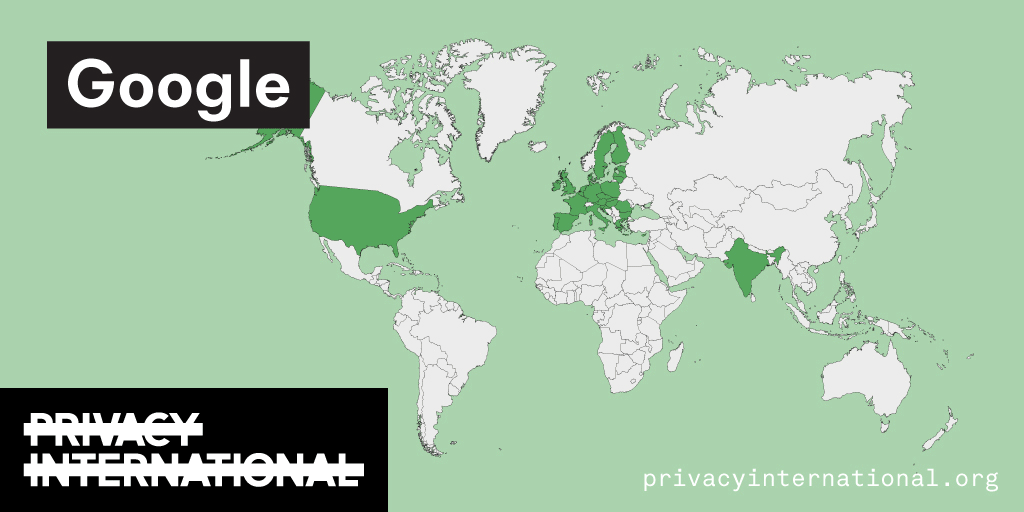
An analysis of what Facebook, Google, and Twitter have done to provide users with political ad transparency as of September 2019. Our full analysis is linked below.
Recently the role of social media and search platforms in political campaigning and elections has come under scrutiny. Concerns range from the spread of disinformation, to profiling of users without their knowledge, to micro-targeting of users with tailored messages, to interference by foreign entities, and more. Significant…
Content Type: Long Read
In December 2018, Privacy international exposed the dubious practices of some of the most popular apps in the world.
Out of the 36 apps we tested, we found that 61% automatically transfer data to Facebook the moment a user opens the app. This happens whether the user has a Facebook account or not, and whether they are logged into Facebook or not. We also found that some of those apps routinely send Facebook incredibly detailed and sometimes sensitive personal data. Again, it didn’t matter if…
Content Type: Case Study
This time, Amtis travels to year 2030 to get a sense of how the data rights framework played out:
I just moved into a new apartment and everything was a mess. My stuff was all over the place and I couldn't find anything. I received a notification on my dashboard that a delivery drone had arrived with my package.
Data rights dashboard
The dashboard showed me a summary report with information about how my data was handled: which company processed my order, the type of data that was collected…
Content Type: News & Analysis
In December 2018, we revealed how some of the most widely used apps in the Google Play Store automatically send personal data to Facebook the moment they are launched. That happens even if you don't have a Facebook account or are logged out of the Facebook platform (watch our talk at the Chaos Communication Congress (CCC) in Leipzig or read our full legal analysis here).
Today, we have some good news for you: we retested all the apps from our report and it seems as if we…
Content Type: News & Analysis
Palantir and the UN’s World Food Programme (WFP) are partnering for a reported $45 million. Palantir, a US-based company that sells data software and has been the centre of numerous scandals.
The World Food Programme provides assistance in food and nutrition to around 92 million people each year. Systems that are produced in agreements such as the one between WFP and Palantir increase risks to the people the they are attempting to help. There are risks to both individuals and whole populations…
Content Type: Examples
In April 2018, the Austrian cabinet agreed on legislation that required asylum seekers would be forced to hand over their mobile devices to allow authorities to check their identities and origins. If they have been found to have entered another EU country first, under the Dublin regulation, they can be sent back there. The number of asylum seekers has dropped substantially since 2016, when measures were taken to close the Balkan route. The bill, which must pass Parliament, also allows the…
Content Type: Examples
In a report on mobile security updates, the US Federal Trade Commission finds that because of the complexity of the mobile ecosystem applying security updates to operating system software on some mobile devices is time-consuming and complicated. Based on information gathered from eight device manufacturers - Apple, Blackberry, Google, HTC, LG, Microsoft, Motorola, and Samsung, the FTC recommends that manufacturers should deploy these updates more quickly and suggests that manufacturers should…
Content Type: Impact Case Study
What is the problem
For over two decades we have been documenting an alarming use and spread of surveillance. It is no longer just the wars on terror or drugs or migration that is driving this trend. The management of health crises and distribution of welfare regularly are among others being used to justify this turn to increasingly invasive forms of surveillance. From country to country we see the same ideas and the same profiteers expanding their reach.
When we first released our report on…