A guide to getting your data from Telegram
Your Telegram app stores a lot of information about you in the cloud. Here we show you how to gain access to it.
The information you (consciously or not) share with Telegram can be very revealing. It can also be (mis)interpreted by government agencies and used to profile individuals. Once installed on a device, depending on your settings, the Telegram app may have access to information such as your location, contact information and media stored on the same device. All of this data can be potentially be accessed remotely using cloud extraction technology.
Your Telegram app generates a lot of data that can also be stored on your device and elsewhere. It’s important for you to be able to understand the types of data that apps like Telegram generate. Government agencies may seek access to this data through at least two routes: they could directly access your device and then analyse the data stored in the app and data your app shares and can access on Telegram’s servers (and potentially data backed-up to your cloud provider) using ‘cloud extraction’ techniques, or they may request your data from Telegram directly.
Tools such as the Oxygen Forensic Cloud Extractor can be used to acquire “data from the most popular cloud services” including WhatsApp, iCloud, Google, Microsoft, Mi Cloud, Huawei, Samsung, E-Mail (IMAP) Servers and more - “also various social media services are supported to include but not limited to: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and many more.”
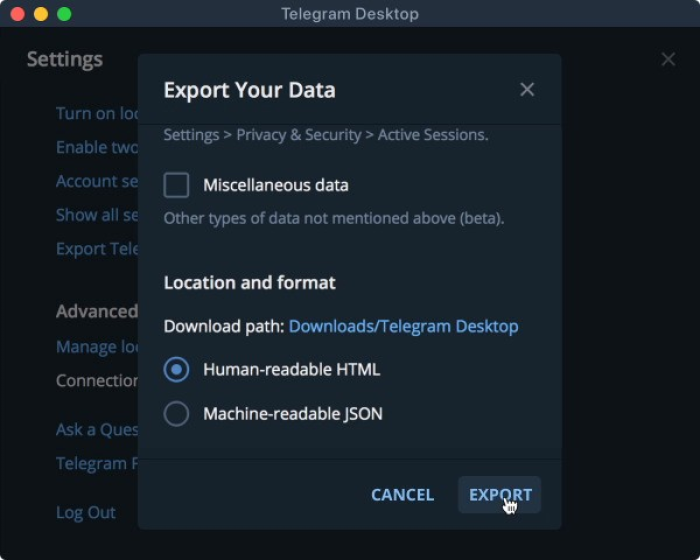
How to find out what data Telegram stores about you
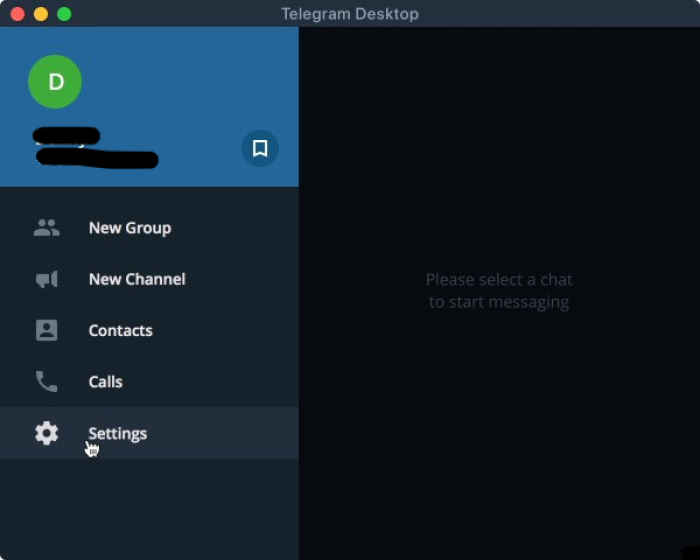
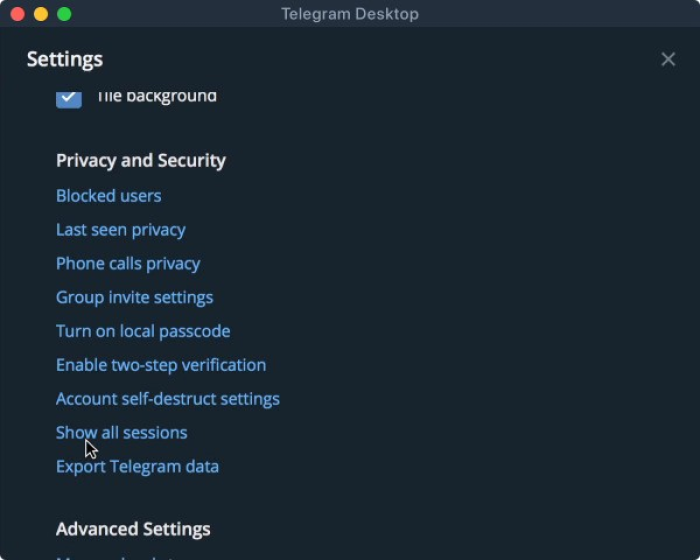
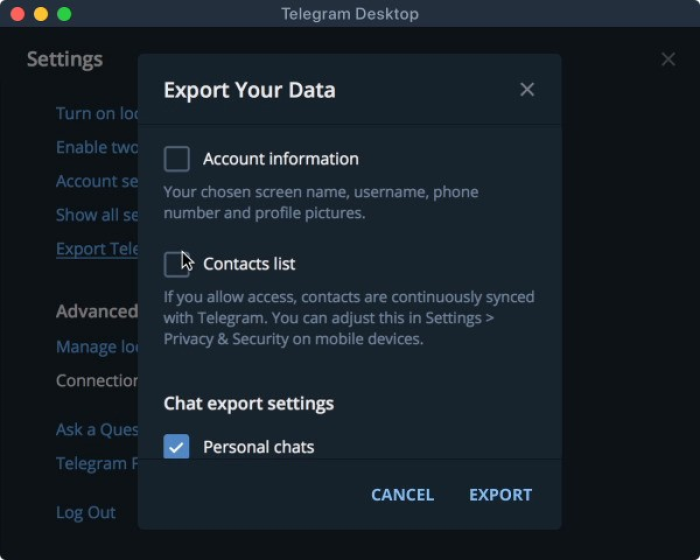
a) In order to be able to access your data, you will need to download the Telegram desktop app. You will not be able to access your data from the phone app itself. If you are on macOS, you need to install the cross-platform version of Telegram (which you can get from here).
b) Open your Telegram desktop app and ensure you are signed into your Telegram account.
Limiting data Telegram collects about you
a) Unfortunately, you cannot limit the location data that Telegram collects about you.
b) However, if you want to find out more about the steps you can take to safeguard your privacy whilst using Telegram, you can read our Telegram good practices guide.
Found a mistake? An outdated screenshot? Think this could be improved? Check out our Github repository and contribute to help keep these guides up-to-date and useful!