Data should be protected
Data should be protected from access by persons who are not the user.
As computing becomes embedded everywhere, privacy, security and safety issues converge. In the future, our infrastructure will be insecure and unsafe due to insecure devices and components that are not patched.
What's the problem?
As more devices become ‘connected’ and services become ubiquitous, they may generate and collect massive amounts of data in excess of what is necessary for the provision of the specific service or function. For instance, the “always on” nature of connected or smart devices and the granularity of data collected potentially enables the provider and other parties access to vast types and volumes of data.
A mere software update or change in business practice can change the frequency of sharing and the parties to whom data can be transmitted can change at any point in time.
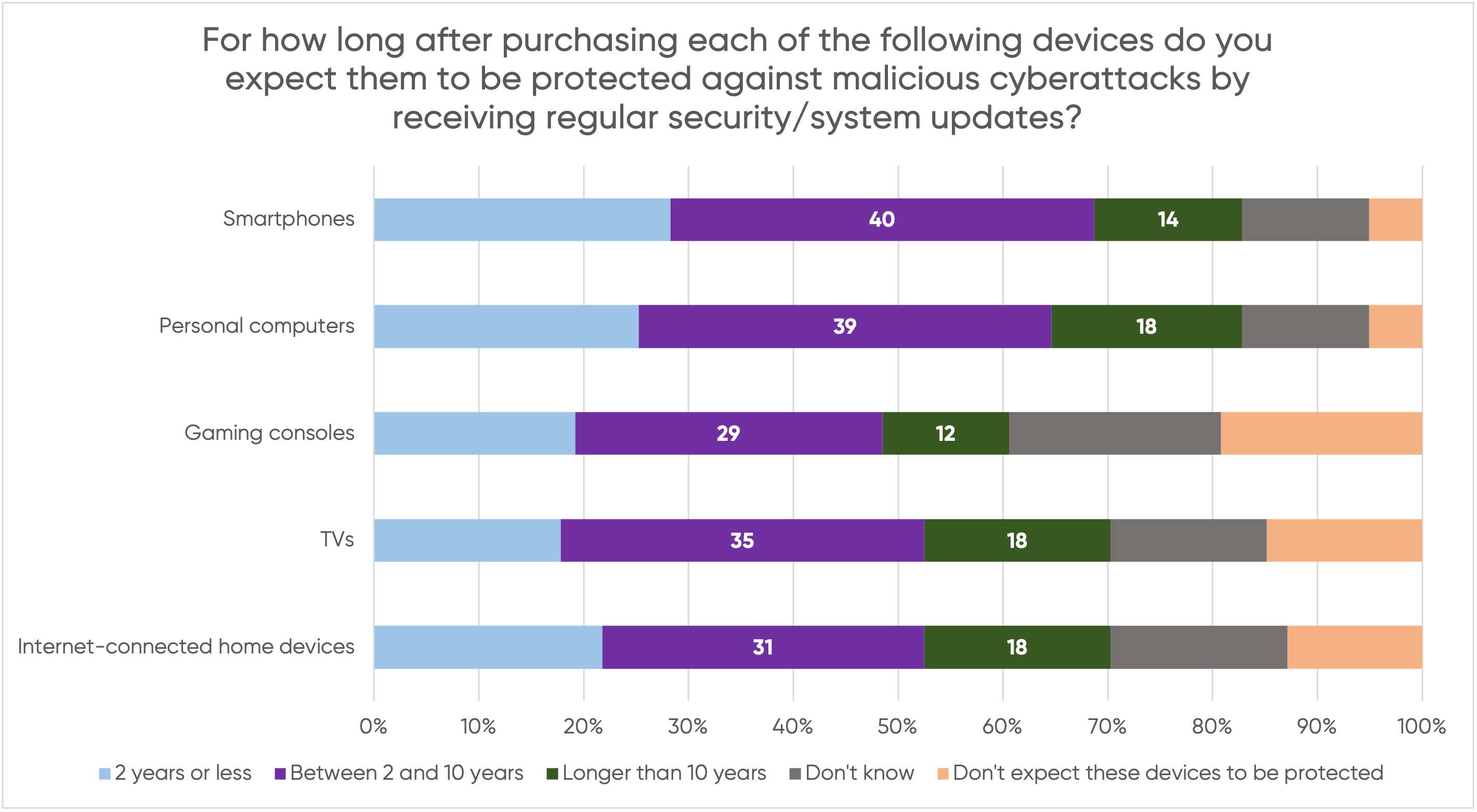
Securing these technologies becomes even more challenging as they are embedded in complex systems, difficult to alter or update for security purposes, and control by the individual is limited. Too often companies decide for business reasons they will no longer support the software or hardware, including for security updates when vulnerabilities are found, leaving consumers unprotected.
This creates an unsafe environment. Unpatched, insecure, and unmaintained systems and infrastructure leave us vulnerable.
What we would like to see
End-to-end encryption will be the default in devices, networks and platforms for data in-transit and at-rest. If deviation from the default is to occur, other essential and equivalent safeguards in law are required.
Data minimisation will be implemented across all devices and platforms by design. Less data generation and processing means that less data that can be misused or breached.
Security researchers will be able to and encouraged to test the products and services to break security and privacy. Open and transparent security research identifies defences necessary for cyber-physical security and safety and challenges information asymmetry.
Cyber security will be considered a common good, which benefits everyone. Policies and initiatives must not advantage only some people over others. This means that a national government policy should not disadvantage people outside that country, or certain sectors of society.
What this will mean
Cybersecurity policies must ensure that they protect all people across economic and geographic boundaries and promote end-to-end encryption.
Why this matters
In the future, our infrastructure will be insecure and unsafe due to insecure devices and components that are not patched. Manufacturers are not held responsible, vendors do not question the security of their products, and supply chain problems are left unaddressed.
There are too few incentives to implement and increase security. Even the companies who take security relatively seriously by doing bug bounties and updates often phase out the patching of security of software and devices after a period of time that has never been made clear to the public.
Too often marginalised communities have to use technologies that do not receive security updates in a timely manner, if at all or have to incur additional costs. Users should be able to accept updates without having to worry that it also adds functionalities that might be privacy-invasive or otherwise against the interest of the user.
Essential reform actions
Companies will have to notify individuals of the life-span of technologies and the period for which they will maintain security updates.
Cybersecurity policies must ensure that they protect all people across economic and geographic boundaries and promote end-to-end encryption.