Advanced Search
Content Type: Long Read
The European Union (EU) spends billions on research and development aimed at driving economic growth and jobs, as well as furthering the bloc’s broader agenda. Within the current budget, known as Horizon 2020 and covering the years 2014-2020, some €80 billion has been made available for research in a huge number of areas, ranging from finding cures for diseases to helping keep the earth viable for life.
From the same budget, it also funds a lot of projects aimed at developing surveillance…
Content Type: News & Analysis
Privacy shouldn’t be a luxury.
Google claim to agree with us - we know that because Sundar Pichai, their CEO, said so this May in the New York Times. And yet, Google are enabling an ecosystem that exploits people who own low-cost phones.
Today we, along with over 50 organisations including Amnesty International, DuckDuckGo, and the ACLU are asking Google to step up, and we’re asking you to join us in pressuring them to do the right thing.
Sign the petition
Google has the power to…
Content Type: News & Analysis
Cloud extraction allows law enforcement agencies to take huge amounts of your data from the Cloud via a legal back door. If law enforcement seize your phone or take it from a victim of crime, they can extract tokens or passwords from the device which lets them get access to data from apps such as Uber, Instagram, Slack, Gmail, Alexa and WhatsApp.
In so doing, law enforcement agencies can avoid official channels through cloud companies such as Google, Apple…
Content Type: Press release
A large number of apps on smart phones store data in the cloud. Law enforcement can access these vast troves of data from devices and from popular apps with the push of a button using cloud extraction technology.
Mobile phones remain the most frequently used and most important digital source for law enforcement investigations. Yet it is not just what is physically stored on the phone that law enforcement are after, but what can be accessed from it, primarily data stored in the Cloud.…
Content Type: Long Read
Following a series of FOI requests from Privacy International and other organisations, the Department of Health and Social Care has now released its contract with Amazon, regarding the use of NHS content by Alexa, Amazon’s virtual assistant. The content of the contract is to a big extent redacted, and we contest the Department of Health’s take on the notion of public interest.
Remember when in July this year the UK government announced a partnership with Amazon so that people would now…
Content Type: Long Read
Photo by Nadine Shaabana on Unsplash
Digital identity providers
Around the world, we are seeing the growth of digital IDs, and companies looking to offer ways for people to prove their identity online and off. The UK is no exception; indeed, the trade body for the UK tech industry is calling for the development of a “digital identity ecosystem”, with private companies providing a key role. Having a role for private companies in this sector is not necessarily a problem: after all, …
Content Type: Long Read
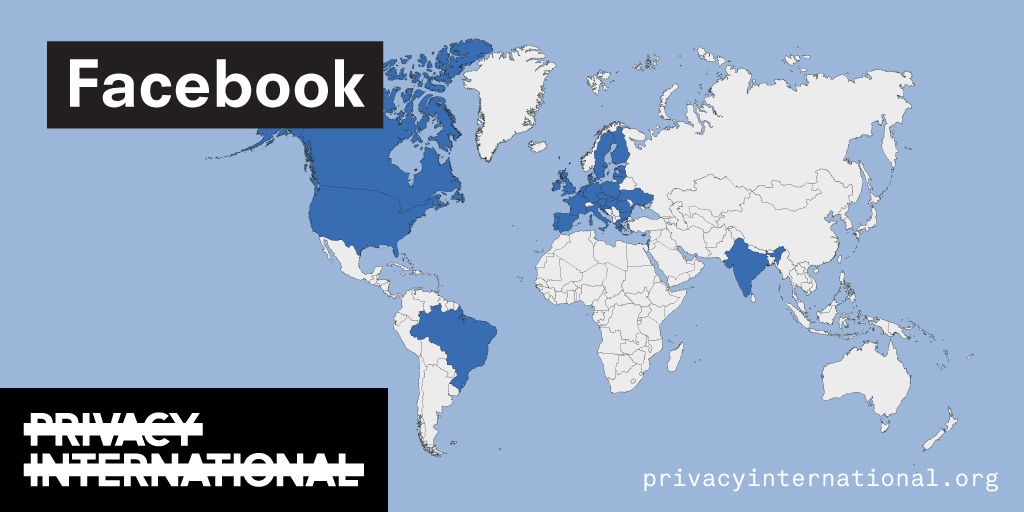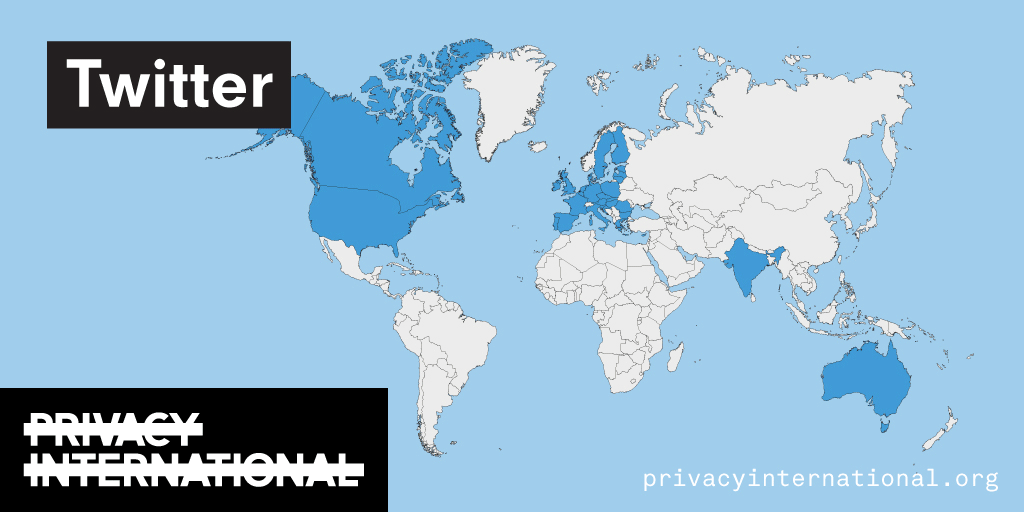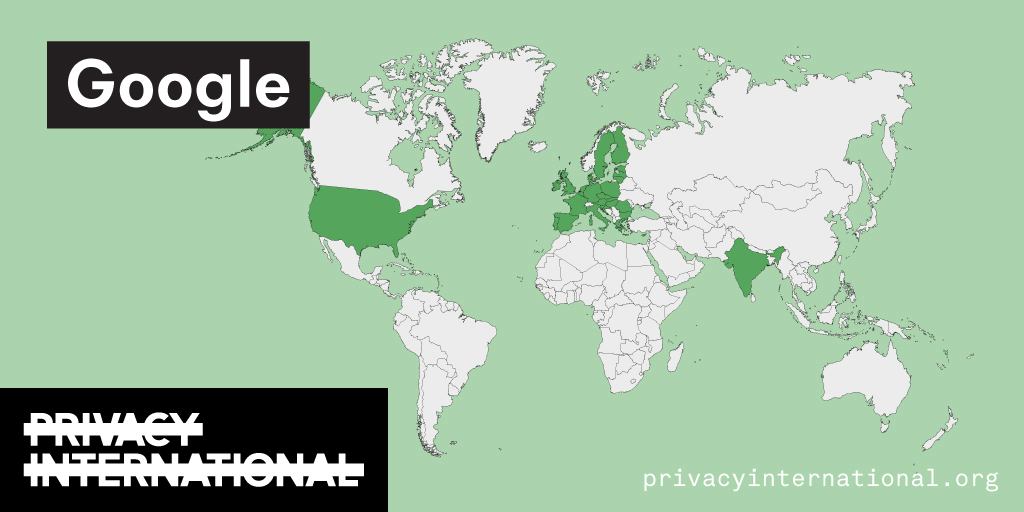
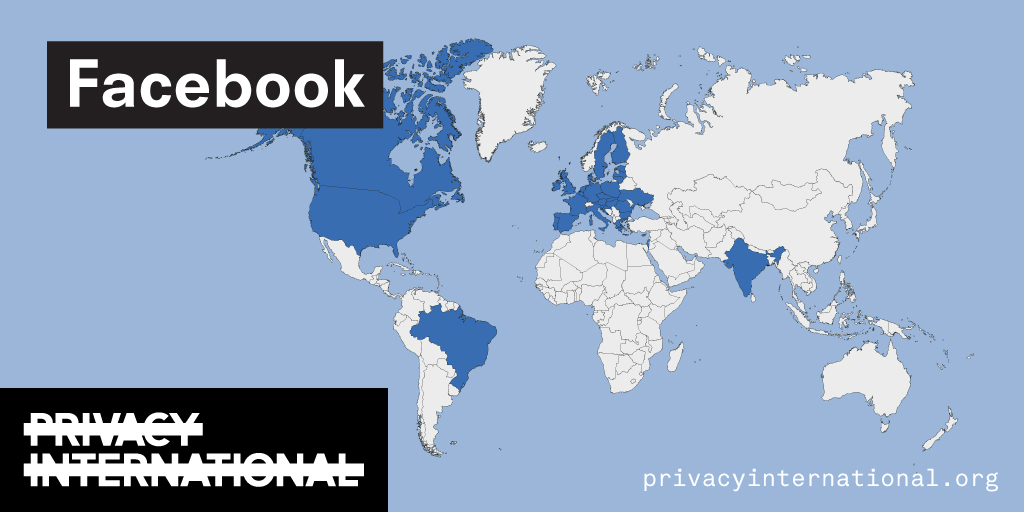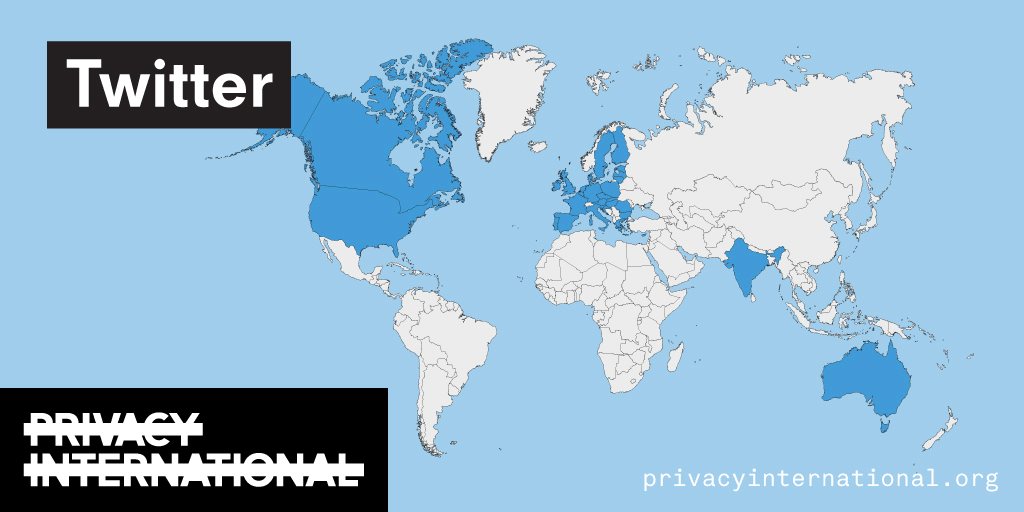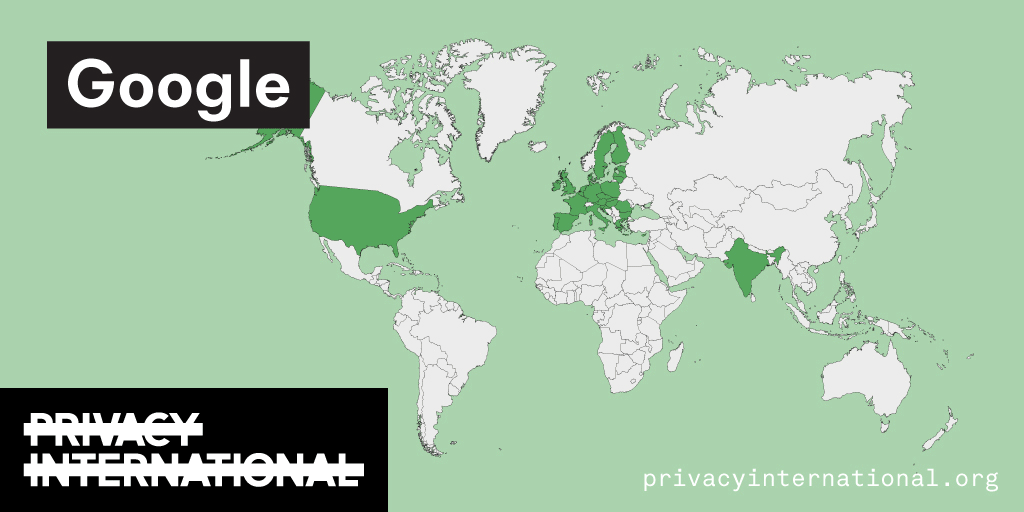
An analysis of what Facebook, Google, and Twitter have done to provide users with political ad transparency as of September 2019. Our full analysis is linked below.
Recently the role of social media and search platforms in political campaigning and elections has come under scrutiny. Concerns range from the spread of disinformation, to profiling of users without their knowledge, to micro-targeting of users with tailored messages, to interference by foreign entities, and more. Significant…
Content Type: Video
Christopher Weatherhead and Eva Blum-Dumontet Discuss the finding of Privacy International's report on the MyPhone MYA2 from the Philippines
Content Type: Long Read
In December 2018, Privacy international exposed the dubious practices of some of the most popular apps in the world.
Out of the 36 apps we tested, we found that 61% automatically transfer data to Facebook the moment a user opens the app. This happens whether the user has a Facebook account or not, and whether they are logged into Facebook or not. We also found that some of those apps routinely send Facebook incredibly detailed and sometimes sensitive personal data. Again, it didn’t matter if…
Content Type: News & Analysis
According to the International Organization for Migration, an estimated 258 million people are international migrants – that is, someone who changes their country of usual residence, That’s one in every 30 people on earth.
These unprecedented movements levels show no sign of slowing down. It is predicted that by 2050, there will be 450 million migrants across the world.
Nowadays, it is politically acceptable to demonise migrants, and countless leaders have spewed divisive and xenophobic…
Content Type: Long Read
Cellebrite, a surveillance firm marketing itself as the “global leader in digital intelligence”, is marketing its digital extraction devices at a new target: authorities interrogating people seeking asylum.
Israel-based Cellebrite, a subsidiary of Japan’s Sun Corporation, markets forensic tools which empower authorities to bypass passwords on digital devices, allowing them to download, analyse, and visualise data.
Its products are in wide use across the world: a 2019 marketing…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Introduction
Acknowledgment
The State of Surveillance in Tunisia is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and partners.
On 14 February 2023, the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights voiced concern over the deepening crackdown in Tunisia targeting perceived political opponents of President Kais Saied as well as civil society.
We have updated this page to reflect important changes in the state of surveillance in Tunisia.
Key privacy facts
1.…
Content Type: News & Analysis
In December 2018, we revealed how some of the most widely used apps in the Google Play Store automatically send personal data to Facebook the moment they are launched. That happens even if you don't have a Facebook account or are logged out of the Facebook platform (watch our talk at the Chaos Communication Congress (CCC) in Leipzig or read our full legal analysis here).
Today, we have some good news for you: we retested all the apps from our report and it seems as if we…
Content Type: News & Analysis
Campaigners are today calling for urgent action to allow Palestinians to develop an independent telecommunications infrastructure following the release of a report detailing how the Israeli government exerts its existing control to rule and monitor the online lives of Palestinian people.
‘Connection Interrupted’, produced by Privacy International partner organisation 7amleh, describes how the Israeli government restricts key telecommunications infrastructure in Palestine,…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgement
The State of Privacy in Uganda is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and Unwanted Witness.
Key privacy facts
1. Constitutional privacy protection: The constitution contains an explicit protection of the right to privacy (Art. 27).
2. Data protection law: There is no…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgment
The State of Privacy in South Africa is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and the Right2Know coalition.
Key Privacy Facts
1. Constitutional privacy protections: Section 14 of the Constitution of the Republic of South Africa protects the right to privacy.
2. Data protection laws…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgement
The State of Privacy in the Philippines is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and Foundation for Media Alternatives.
Key privacy facts
1. Constitutional privacy protection: The constitution contains an explicit protection of the right to privacy (Art. III, section 3).
2.…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgment
The State of Privacy in Pakistan is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and the Digital Rights Foundation.
Between 2014-2016, Bytes for All contributed to previous versions of the 'Data Protection' sections of this briefing.
Key Privacy Facts
1. Constitutional privacy protections: Article 14(1) of…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgment
The State of Surveillance in Morocco is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and its partners.
Key privacy facts
1. Constitutional privacy protection: The constitution contains an explicit protection of the right to privacy.
2. Data protection law: There is a data…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgement
The State of Privacy in Mexico is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and Red in Defensa de los Derechos Digitales (R3D) in Mexico.
Key Privacy Facts
1. Constitutional privacy protections: The right to privacy is enshrined in article 6 of the Mexican constitution.
2. Data…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgement
The State of Privacy in Kenya is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and the National Coalition of Human Rights Defenders - Kenya.
Key Privacy Facts
1. Constitutional privacy protections: Article 31 of the Kenyan Constitution specifically protects the right to privacy.
2. Data…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgement
The State of Privacy in Jordan is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and 7iber.
Key privacy facts
1. Constitutional privacy protections: Article 18 of the Jordanian constitution contains an explicit mention of privacy.
2. Data protection laws: There is currently no data…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgment
The State of Privacy in Indonesia is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and The Institute for Policy Research and Advocacy (ELSAM).
Key privacy facts
Key privacy facts
1. Constitutional privacy protection: The constitution does not explicitly mention privacy.
2. Data protection…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgement
The State of Privacy in India is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and the Centre for Internet & Society.
Key Privacy Facts
1. Constitutional privacy protections: In 2017, the Indian Supreme Court ruled that the Indian constitution guarantees a right to privacy.
2. Data…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Table of contents
Introduction
Right to Privacy
Communication Surveillance
Data Protection
Identification Schemes
Policies and Sectoral Initiatives
Introduction
Acknowledgment
The State of Surveillance in Egypt is the result of an ongoing collaboration by Privacy International and its partners.
Key privacy facts
1. Constitutional privacy protection: The constitution contains an explicit protection of the right to privacy.
2. Data protection law: In August 2018, the Cabinet…
Content Type: State of Privacy
Introduction
Acknowledgement
The State of Surveillance in Chile is the result of an ongoing collaboration between Privacy International and its Chilean partners Derechos Digitales and Fundación Datos Protegidos.
Key Privacy Facts
1. Constitutional privacy protections: Article 19 of Chile's constitution protects the right to a private life. It was reformed in 2018 to add a specific right to the protection of personal data.
2. Data protection laws: In 1999 Chile became the…
Content Type: Case Study
The exclusion caused by ID can have a devastating effect on people, limiting their opportunities and ability to survive.
Names have been changed.
Carolina is in a more privileged position than many other migrants, she admits that. She has a formal job, for one. She is – and has always been – in Chile legally: her previous visa has expired, and her new one is being processed. Under the law, she is permitted to stay and work in the country while this is happening. But she is finding the…
Content Type: News & Analysis
Why is a privacy organisation working with the humanitarian sector, and why does it matter? We may seem like strange bedfellows, but today's ever-growing digital world means that, more and more, people who receive humanitarian assistance are being exposed to unexpected threats.
According to the 2018 Global Humanitarian Overview, there are more than 134 million people across the world in need humanitarian assistance. Of these, about 90.1 million will receive aid of some form. It is…